COVID-19
利用 Google Trends 作為數位生物標誌
Google Trends 關鍵字搜尋量被證明是一種可靠且方便的工具,可用於研究公共興趣和行為趨勢。與傳統方法相比,它具有廣泛且及時的被動數據收集能力,並且具備高時間解析度。我們的研究團隊透過 ARIMA模型,預測在特定事件(如疫情爆發或相關政策)未發生情況下的搜尋量,並將此「預測值」與實際搜尋量進行比較,從而分析事件對搜尋行為的影響,這些數位足跡被視為反映公共行為的數位生物標誌。
Google Trends 關鍵字搜尋量被證明是一種可靠且方便的工具,可用於研究公共興趣和行為趨勢。與傳統方法相比,它具有廣泛且及時的被動數據收集能力,並且具備高時間解析度。我們的研究團隊透過 ARIMA模型,預測在特定事件(如疫情爆發或相關政策)未發生情況下的搜尋量,並將此「預測值」與實際搜尋量進行比較,從而分析事件對搜尋行為的影響,這些數位足跡被視為反映公共行為的數位生物標誌。
2020年COVID-19疫情開始在全球蔓延後,我們的研究團隊便藉由google trends等公開資訊,進行一系列與COVID-19疫情相關的精神醫學研究。
我們的研究包括透過「洗手」的網路搜尋量分析疫情傳播速度;以及用「失眠」、「憂鬱」、「自殺」三個心理健康的關鍵字的搜尋量作為心理健康指標,發現「失眠」是世界各國受疫情影響心理健康最敏感的指標;我們也利用開放資料庫所記錄的手機定位量化疫情期間不同國家的居家限制外出程度,並將此指標作為中介因子進行因果分析,發現「居家限制外出」程度是疫情影響心理健康最重要的中介因子,此結果對居家限制外出政策未來可能的彈性調整提供了醫學實證基礎。
我們針對Covid-19進行了上述各項研究,成果皆刊登於國際醫學期刊,展示、證明了數位足跡在疫情期間作為人口行為指標的重要性,也為制定更靈活且有科學依據的公共衛生政策提供了關鍵洞察與實證依據。
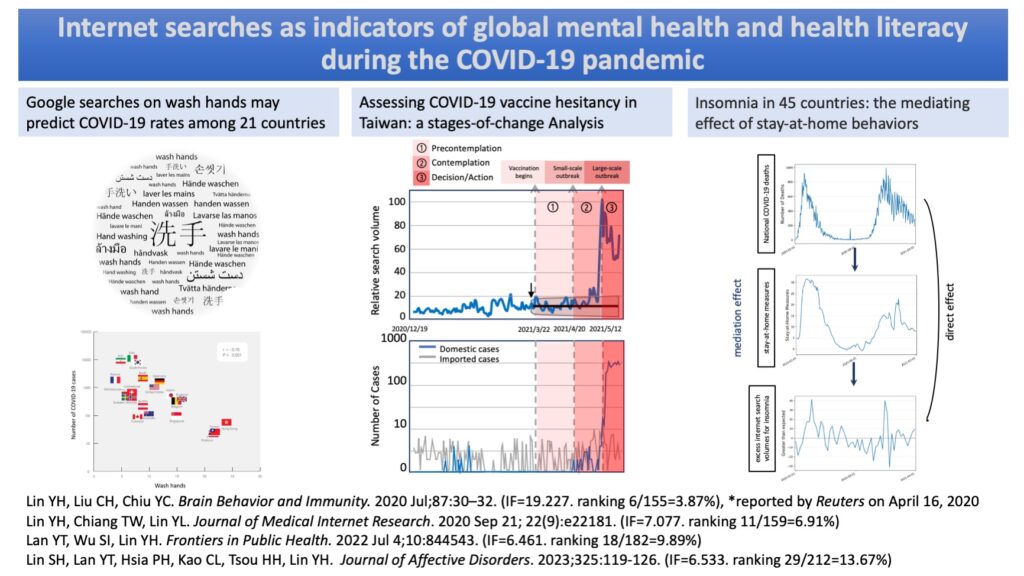

居家行為是疫情影響心理健康的主要中介因子
研究發現,疫情期間居家行為的程度是疫情嚴重程度對心理健康影響的主要中介因子。研究團隊利用 Google Trends 上「失眠」與「自殺」的搜尋量作為心理健康指標,發現疫情初期居家行為顯著影響失眠的增加(中介比例為 42.6%,p=0.016),而在疫情後期,居家行為對自殺率的減少有顯著中介作用(中介比例為 39.6%,p=0.014)。這些結果顯示,疫情期間居家行為的影響具有動態性,並為調整居家政策提供了實證依據。

台灣疫苗施打意願隨本土疫情變化而轉變
我們發現,從民眾在網路對「疫苗」的搜尋量可以反映、並持續追蹤大眾的疫苗施打意願。我們分析了 2021 年 3 月至 5 月期間台灣的 Google Trends 數據,發現疫苗搜尋量與本土確診病例數高度相關(r=0.71, P<.001)。疫苗施打意願的變化可以對應到行為改變的不同階段:前考慮階段(2021年3月19~4月19):疫情未擴散,疫苗搜尋量和施打率均低,顯示大眾尚未積極考慮施打疫苗。
考慮階段(4 月 20 日至 5 月 11 日):小規模區域疫情爆發,搜尋量和施打率上升,表明民眾開始權衡施打疫苗的利弊,搜尋關鍵字多集中在「副作用」。
決策與行動階段(5 月 12 日至 5 月 25 日):台灣本土大規模疫情爆發,搜尋量和施打率顯著提升,搜尋多集中在「預約疫苗」和 AstraZeneca 疫苗的相關資訊。
COVID-19防疫政策
Google trends 提供過去無法透過傳統調查方法呈現出的群眾行為與觀點,這些數位足跡幫助我們更加全面地貼近並理解大眾對疫情的反應,以及各項國家公共政策與公衛措施的影響及有效性。而透過監測、分析開放資料庫的各種數位足跡,我們也為評估COVID-19防控政策的有效性作出了貢獻。
在我們其中一項研究中,我們使用了Google趨勢中「洗手」、「口罩」及「失眠」的搜尋量數據,作為評估COVID-19政策的國家健康素養及心理健康趨勢指標。這項研究涵蓋了全球50多個國家或地區,分析了疫情前兩年的防疫政策。我們在敏感性分析中加入Google趨勢的健康素養及失眠相關指標後,這些指標略微改變了50個國家防疫表現的整體排名,顯示出大眾對相關議題的關注及搜尋行為,這對於理解一個國家的疫情準備與應對能力具有重要的參考價值(Tsou et al., 2022)。
而我們也持續利用Google移動數據報告做出另一份研究,觀察人們在不同COVID-19警戒級別及政策干預下,大眾移動與聚集行為的變化。在台灣,當台北市與新北市進入三級警戒後,各種銷售場所、娛樂場所、公園、交通樞紐及工作場所的人流量顯著減少。2021年5月15日全台灣實施三級警戒後,平均每日移動次數急劇下降,尤其是在都市地區。我們發現台北市的每日移動次數減少了52%,而全台灣的每日移動次數也平均下降了28%。這些數據顯示,在嚴格的隔離管制措施前後,台灣民眾在疫情期間就主動減少活動與聚會,以此作為防疫的措施。此外,儘管2022年初Omicron變異株出現,台灣的住院率及死亡率依然保持低標,在Google的移動數據報告中,台灣社會整體仍呈現著正常的生活模式,充分展現出台灣的公共衛生措施及民眾反應成功地減輕了Omicron變異株對群體健康帶來的影響(Tsou等人,2024。)
歡迎點擊右方影片或下方連結,收聽我們製作的podcast,了解我們過去利用Google Trends資料進行疫情期間全球公衛政策及大眾心理健康的研究成果。
在這集節目中,我們從Google Trends關鍵字搜尋量出發,探討疫情期間全球與台灣的數位足跡如何反映公衛政策的成效與民眾反應。從搜尋「口罩」、「失眠」到「疫苗」等等,我們分析了數據背後的行為轉變,並揭示這些數位指標如何補足傳統調查的盲點,為COVID-19政策評估提供嶄新視角。
論文發表
1. Causal mediation analysis for difference-in-difference design and panel data.
Hsia PH,Tai AS, Kao CL, Lin YH, Lin SHEpidemiol. Methods 2025; 14(1): 20240025
應用於差異中的差異設計與縱橫資料的因果中介分析:以 COVID-19 疫情對心理健康之影響為例
2.Cross-Correlation Analysis of Monthly Google Search Volume and Suicide in Taiwan, 2012–2022
Yen CF, Lin YH, Hsiao RC, Chen YY, Chen YL
Depression and Anxiety, 2025, 5515746, 9 pages, 2025.
2012至2022年台灣每月Google搜尋量與自殺率之交叉相關分析
3. Search Volume of Insomnia and Suicide as Digital Footprints of Global Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Lin S, Su K, Tsou H, Hsia P, Lin Y
Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2025;27:e67646.
以COVID-19 疫情期間「失眠」與「自殺」搜尋量作為全球心理健康數位足跡的三年資訊流行病學研究
4. Internet Searches for “Insomnia” and “Suicide” Mediated by Stay-at-Home Behaviors in 45 Countries during the First 12 Months of the COVID-19 Pandemic Hesitancy During the COVID-19 Outbreaks
Lin SH, Lan YT, Hsia PH, Kao CL, Tsou HH, Lin YHJournal of Affective Disorder. 2023;325:119-126.疫情爆發全球45國「失眠」與「自殺」網路搜尋行為之居家防疫中介效果分析
【探索大腦的會談地圖podcast】待在家裡的程度是疫情影響心理健康的重要因素
5. Utilizing Internet Search Volume to Monitor Stages of Change in Vaccine Hesitancy During the COVID-19 Outbreaks
Lan YT, Wu SI, Lin YH
Frontiers in Public Health. 2022;10:844543.
利用網路搜尋量監測 COVID-19 疫情期間疫苗猶豫的變化階段
你是在什麼時候決定要打疫苗呢?或是你也正在擔心哪些親朋好友還沒有打疫苗?(2022年7月5日)
6. Efficiency and Quality of Data Collection Among Public Mental Health Surveys Conducted During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Systematic Review
Lin YH, Chen CY, Wu SI.
Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2021;23(2):e25118.COVID-19 疫情期間公共心理健康調查的資料蒐集效率與品質:系統性回顧
Covid-19與心理健康方法學之系統性回顧
7. Increased Internet Searches for Insomnia as an Indicator of Global Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Multinational Longitudinal Study.
Lin YH, Chiang TW, Lin YL. 2020;22(9):e22181
Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2020;22(9):e22181
以COVID-19 疫情期間失眠搜尋量增加作為全球心理健康指標
【報導者 The reporter】網路搜尋「失眠」,是疫情期間心理健康預測指標。(2020年9月24日)。
8. Google Searches for the Keywords of “Wash Hands” Predict the Speed of National Spread of COVID-19 Outbreak Among 21 Countries.
Lin YH, Liu CH, Chiu YC.
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2020; 87: 30–32.
以「洗手」的Google搜尋量預測COVID-19於21國傳播速度之研究
【The News Lens關鍵評論】 Google趨勢:哪國「洗手」搜尋量較多?和後續的疫情控制有關係嗎? (2020年4月19日)
【延伸研究】 Google trends: 中國軍事活動如何影響台灣民眾心理健康
1. Perceived threat of potential military conflicts between Taiwan and China and psychological distress among Taiwanese individuals: A population-based study.
Cheng-Fang Yen, Ray C. Hsiao, Yu-Hsuan Lin
Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences(2024).面對中國與台灣之間的軍事衝突為台灣民眾帶來的威脅感受與心理壓力:一項人口研究。
2. Associations of China’s Military Activities in the Peripheries of Taiwan With Suicide Death and Internet Searches for Depression, Suicide, and Emigration Among Individuals in Taiwan.
Yen CF, Lin YH, Hsiao RC, Chen YY, Chen YL.
Asian J Psychiatry. 2024; 92: 103889.面對中國與台灣之間的軍事衝突為台灣民眾帶來的威脅感受與心理壓力:一項人口研究。【探索大腦的會談地圖podcast】中國近年的軍事活動影響台灣人網路搜尋「移民」與「憂鬱」增加
3. Associations of China’s Military Activities in the Peripheries of Taiwan With Suicide Death and Internet Searches for Depression, Suicide, and Emigration Among Individuals in Taiwan.
Lan YT, Wu SI, Lin YHFrontiers in Public Health. 2022;10:844543.中國軍事行動對臺的影響及臺灣自殺死亡率、憂鬱、自殺與移民相關搜尋行為之關聯性研究